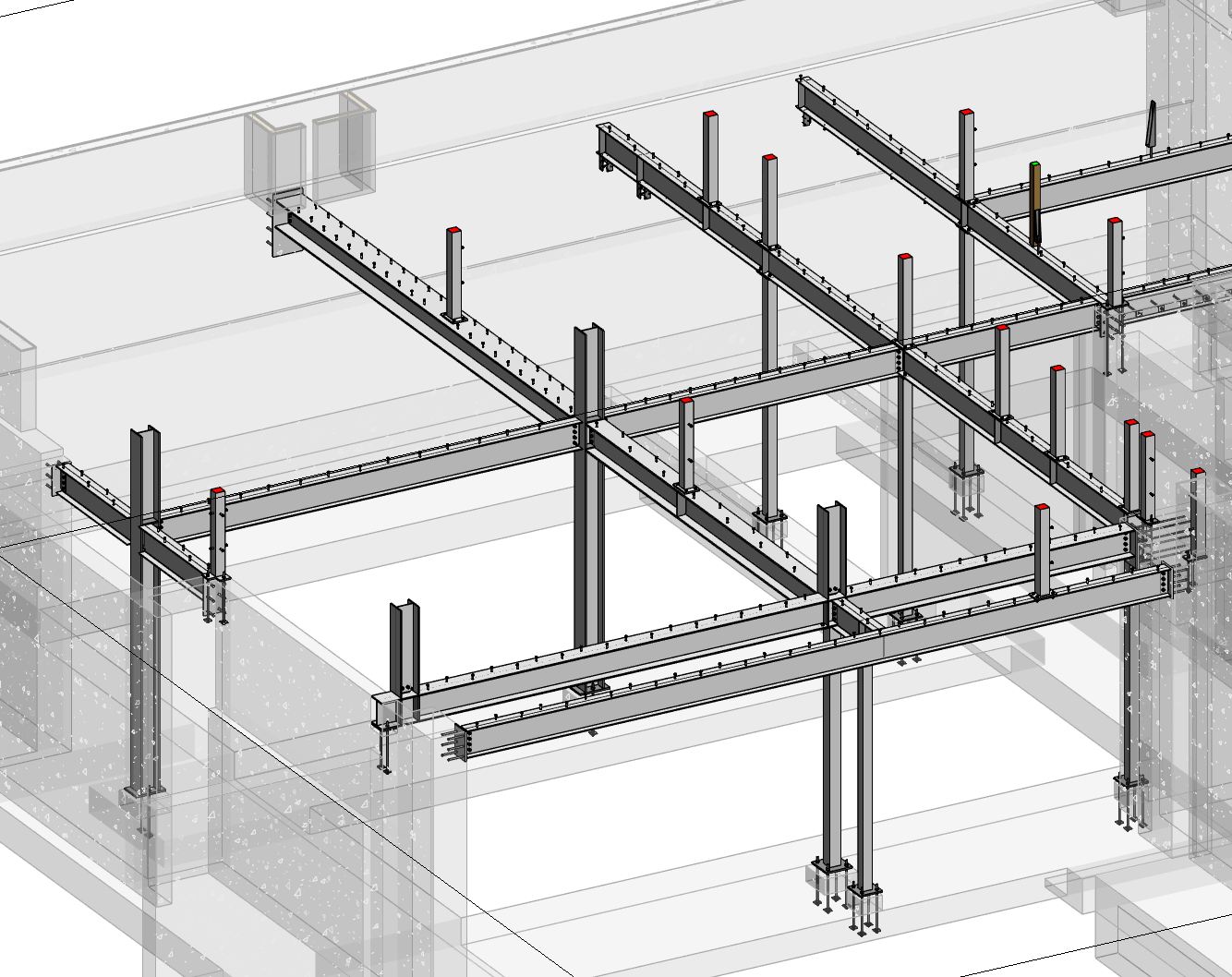
Successful steel fabrication and erection is based on steel shop drawings. They convert structural design intent to build-ready directions that are used daily by fabricators and erectors. Nonetheless, the most elaborate shop drawings may create costly mistakes, timeline or construction problems, when they do not entirely meet industry requirements. Here is where compliance in AISC code comes in.
The American Institute of steel construction (AISC) sets up fairly acceptable standards applicable to the design, manufacture and construction of steel in the United States. The need to ensure the compliance of AISC steel shop drawings is not only a requirement of the regulations but rather a quality standard that protects the structural integrity, constructability, and project efficiency.
This blog discusses the meaning of AISC compliance, its application to steel shop drawings, the pitfalls in compliance and how to practice compliance to be sure that your drawings comply with AISC standards each and every time.
What Is AISC and Why Is It the Industry Standard?
The American Institute of Steel Construction (AISC), is a non-profit organization that produces technical standards, manuals and certification programs to be used in the structural steel industry. The International Building Code (IBC) makes reference to AISC standards and they are used by engineers, fabricators, and inspectors in the U.S.
Key AISC publications influencing steel shop drawings include:
- AISC 360 – Specification for Structural Steel Buildings
- AISC Steel Construction Manual
- AISC 303 – Code of Standard Practice for Steel Buildings and Bridges
The American Institute of Steel Construction (AISC), is a non-profit organization that produces technical standards, manuals and certification programs to be used in the structural steel industry. The International Building Code (IBC) makes reference to AISC standards and they are used by engineers, fabricators, and inspectors in the U.S.
Steel Shop Drawings in the Construction Process
Steel shop drawings are detailed documents prepared by steel detailers based on structural design drawings and specifications. They provide fabricators with precise instructions for cutting, drilling, welding, and assembling steel members.
Typical steel shop drawings include:
- Member details (beams, columns, braces)
- Connection details (bolted and welded)
- Bolt sizes, grades, and spacing
- Weld symbols and specifications
- Material grades and finishes
- Erection marks and piece numbers
AISC code compliance ensures that all of this information follows approved design criteria, fabrication tolerances, and erection standards.
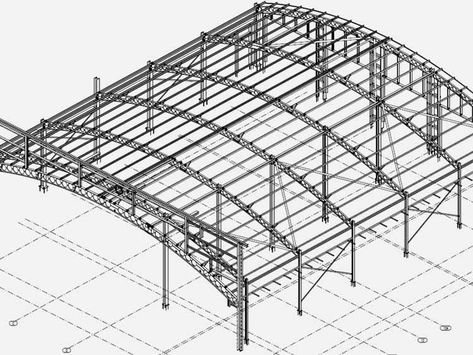
How AISC Code Compliance Applies to Steel Shop Drawings
The compliance of AISC code is important in converting the intent and design of the structure to safe and constructible and buildable steel shop drawings. When AISC requirements are applied correctly, steel shop drawings are no longer technical documents, they have become trusted tools that can be used to direct fabrication and erection process accurately, minimize errors and facilitate a seamless process of the project throughout all its construction phases.
1. Compliance with Design Intent
The AISC standards mandate that shop drawings should be able to clearly show the design intent of the structural engineer. Load path and member sizes and connection behavior should not be altered by detailers without an appropriate approval. Any elaboration should be in line with the controlling structural drawings and specifications.
2. Connection Detailing Requirements
Connections are one of the most critical areas of AISC compliance. Shop drawings must clearly define:
- Bolt type, diameter, grade, and installation method
- Weld sizes, types, and inspection requirements
- Edge distances, spacing, and end distances
- Slip-critical or bearing-type connections
Failure to meet AISC connection standards can result in rejected drawings or unsafe construction.
3. Material Specifications
AISC standards demand adequate identification of the steel grades of ASTM A992, A36, A572 or A500. To make certain that strength, ductility and compatibility between design assumptions and material are maintained, the grades of materials used in shops should be specified.
4. Fabrication and Erection Tolerances
AISC establishes acceptable tolerances for fabrication and erection. Steel shop drawings must accommodate these tolerances to avoid misalignment, fit-up issues, or field modifications.
The Role of AISC 303: Code of Standard Practice
AISC 303 plays a major role in shop drawing compliance by defining responsibilities among project stakeholders. It clarifies:
- Who is responsible for preparing shop drawings
- The level of detail required
- The review and approval process
- Acceptable deviations and revisions
According to AISC 303, shop drawings are not contract documents but are essential for execution. Compliance ensures that drawings provide enough information for fabrication while respecting the engineer’s authority over structural design.
Common AISC Compliance Issues in Steel Shop Drawings
Steel shop drawings are important in converting structural design intent into buildable code-compliant structural steel. Nevertheless, a small mistake in compliance of AISC code may cause errors in fabrications, unsuccessful review, project delay and expensive rework. Others, which are common with compliance, include the situation where the standards, connection requirements, material specifications or tolerances described by the American Institute of Steel Construction are misinterpreted or applied inconsistently.
Incomplete Connection Information
Missing bolt grades, unclear weld symbols, or unspecified installation requirements often lead to rejections during review.
Incorrect Material Designations
Using outdated or incorrect ASTM grades can compromise structural performance and violate AISC requirements.
Non-Compliant Edge Distances and Spacing
Improper bolt spacing or edge distances can weaken connections and fail AISC minimum standards.
Unauthorized Design Changes
Detailers may unintentionally alter connection types or member sizes without engineer approval, leading to compliance violations.
Poor Coordination with Other Trades
Lack of coordination with architectural or MEP elements can result in clashes that require non-compliant field fixes.
The Review and Approval Process for AISC-Compliant Shop Drawings
A review and approval is a significant step towards the complete compliance of steel shop drawings in regards to the AISC standards. This is done at several levels of inspection, where internal quality control is done by detailers, formal inspection by fabricators and the engineer of record.
A check of each stage ensures compliance with the AISC requirements and project specifications with regard to all member dimensions, connection information, material specifications, and fabrication tolerances.
Steel shop drawings typically undergo several layers of review before approval:
- Internal Quality Control
Detailing teams verify dimensions, connections, and materials against AISC standards. - Fabricator Review
Fabricators review drawings for constructability, shop capabilities, and efficiency. - Engineer of Record (EOR) Review
The EOR checks compliance with design intent and AISC requirements. - Revision and Resubmission
Any non-compliant items are revised and resubmitted for final approval.
Following a structured review process significantly improves AISC compliance and reduces delays.
The Role of Software in Ensuring AISC Compliance
Modern steel detailing software such as Tekla Structures and Autodesk Advance Steel plays a major role in maintaining AISC compliance. These tools provide:
- Built-in connection libraries aligned with AISC standards
- Automated bolt and weld checks
- Clash detection and constructability validation
- Accurate material takeoffs and schedules
However, software alone does not guarantee compliance. Experienced detailers must still verify assumptions, apply engineering judgment, and coordinate with project teams..
Benefits of AISC-Compliant Steel Shop Drawings
Ensuring that steel shop drawings comply with AISC standards brings numerous benefits to every stage of a construction project, from design and fabrication to erection and long-term maintenance. Compliance is more than a regulatory requirement—it is a proven approach to enhancing accuracy, efficiency, and safety in steel construction.
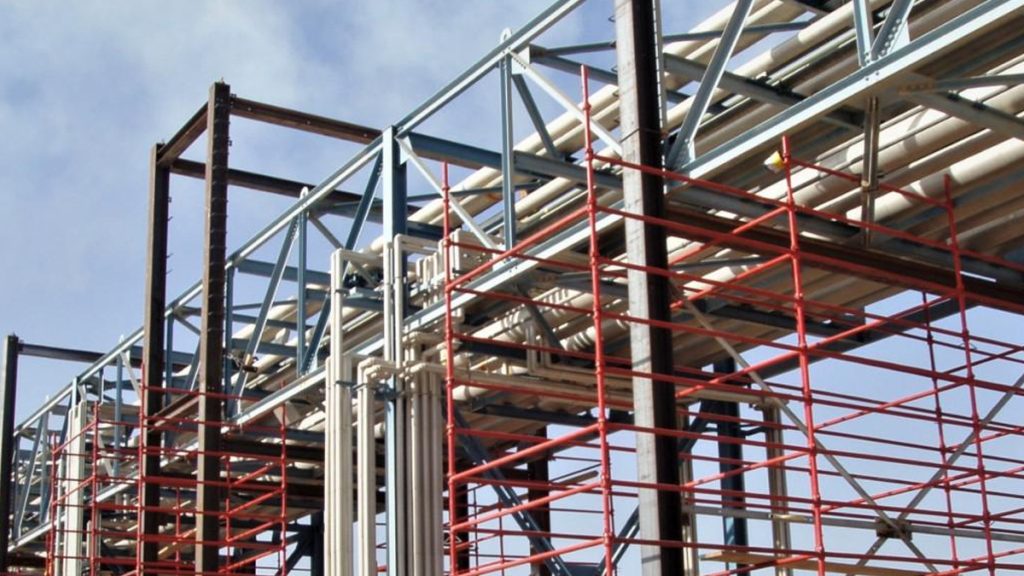

1. Improved Accuracy and Precision
AISC-compliant steel shop drawings provide exact dimensions, connection details, and material specifications. This reduces errors during fabrication and erection, ensuring that each steel member fits perfectly on site, minimizing field modifications.
2. Faster Review and Approval
Drawings that adhere to AISC standards are easier for engineers and inspectors to review and approve. Compliance reduces the number of revisions required, accelerates project timelines, and prevents costly delays.
3. Enhanced Structural Safety
AISC guidelines ensures that all connections, member sizes, and material choices meet structural design requirements. This compliance strengthens overall building integrity and safeguards occupants and assets.
4. Cost Efficiency and Reduced Rework
Non-compliant shop drawings often lead to fabrication mistakes and on-site adjustments. AISC-compliant drawings minimize these issues, helping to reduce labor, material waste, and rework costs.
5. Better Coordination Between Stakeholders
AISC standards provide a common framework for designers, detailers, fabricators, and erectors. Compliant drawings enhance communication, reduce misunderstandings, and ensure that all project stakeholders are aligned.
6. Long-Term Project Reliability
By adhering to AISC codes, steel shop drawings contribute to durable, high-quality construction. Buildings constructed from compliant drawings are easier to maintain, perform reliably, and stand the test of time.
Ultimately, AISC compliance leads to smoother project execution and long-term structural reliability.
AISC Compliance and Risk Mitigation
Non-compliant shop drawings can expose project teams to significant risks, including delays, cost overruns, and liability issues. AISC-compliant drawings reduce these risks by ensuring that all stakeholders operate within a recognized and enforceable framework.
For owners and contractors, compliance offers peace of mind. For fabricators and detailers, it demonstrates professionalism and technical competence.
Conclusion
AISC code compliance in steel shop drawings is not a box-checking exercise. It is a fundamental requirement that directly impacts safety, constructability, and project success. From accurate connections to proper material specifications, every detail matters.
By understanding AISC standards, leveraging modern software, and following best practices, project teams can produce steel shop drawings that meet regulatory expectations and deliver real-world value. In an industry where precision matters, AISC compliance is the standard that keeps steel construction strong, safe, and reliable.