Building Information Modeling (BIM) has transformed the architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) sector since it allows representatives to operate digital models of physical and functional features of buildings. As it develops, BIM adds multi-dimensional layers, which greatly exceed mere 3D visualization. Every dimension introduces a new layer of information and usefulness, assisting teams to plan, build and operate buildings more effectively.
This blog will describe the most popular BIM dimensions, namely 3D, 4D, 5D, 6D, and 7D, their meaning, functionality, and involvement in the life of a building project.
3D BIM – Visual Representation and Design Coordination
The 3D BIM is the base dimension that deals with geometric modeling. It will allow the stakeholders to have a 3D (length, width, and height) model of the physical structure.
Contrary to the usual 2D blueprints, a 3D model provides a full view of all the structural and aesthetic components of a building, limiting confusion in the design review process. Our BIM consulting goes beyond visualization – it’s a collaboration tool in which many disciplines can intersect. Load paths can be verified by structural engineers, services can be routed through ceiling voids by MEP designers, and furnishings can be aligned by interior designers, all in the same model powered by our modeling services.

What it does:
- Enhances collaboration through shared design models
- Allows early-stage clash detection among architectural, structural, and MEP systems
- Improves accuracy in design and spatial planning
Key Tools: Autodesk Revit, ArchiCAD, SketchUp, Rhino
4D BIM – Construction Scheduling
4D BIM is an addition of time aspect to the 3D model, allowing the scheduling of projects and construction ordering. Using 4D BIM, stakeholders are able to model out the whole process of construction even before the first shovel goes into the ground. Construction teams can actually see how a building will come together in days, weeks, or months by allocating each building element to a particular timeline or schedule.
The visualization of this timeline allows for identifying the possible clashes, e.g. the wall is built before the foundation is poured, and to plan the material, equipment, and labor resources more efficiently. The 4D BIM allows contractors to produce visual Gantt charts or animations to exactly describe the project milestones to clients and investors.
What it does:
- Links construction tasks to the 3D model components
- Simulates project timelines and construction activities
- Identifies schedule conflicts and bottlenecks
Key Tools: Navisworks, Synchro 4D, Bentley ConstructSim
5D BIM – Cost Estimation and Budget Management
5D BIM is the model that incorporates cost information into the 3D and 4D model to enable real-time cost estimation and budget evaluation. Whether it is materials and labor, equipment, and overhead, 5D BIM allows dynamic budgeting that will be changed in real-time depending on the changes made in the design. To illustrate, when a structural element is changed, the 5D model will reconstruct related costs in real-time, feedback to the project team. This minimises the chances of cost overruns and scope creep.
Also, 5D BIM enhances client confidence through the transparency of cost forecasting and provides value engineering options without affecting the design integrity. It is also tremendously useful during the bidding procedure, where contractors may give more competitive and precise bids. The 5D BIM facilitates the management of costs through the supply chain in a seamless manner when it is integrated with procurement systems.
What it does:
- Provides dynamic cost calculation as the model evolves
- Allows real-time budget tracking and forecasting
- Enhances transparency between stakeholders regarding project finances
Key Tools: Vico Office, CostX, Autodesk Quantity Takeoff
6D BIM – Sustainability and Energy Analysis
6D BIM is associated with the green effect of the construction. It contains information on sustainable practice, energy modelling and life cycle assessment (LCA). With the growing concern of achieving sustainability across the globe, 6D BIM is taking a central role in ensuring that the construction industry achieves environmental targets. It provides an intelligence layer that is concerned with the Carbon footprint, energy performance, and the lifecycle sustainability of the building.
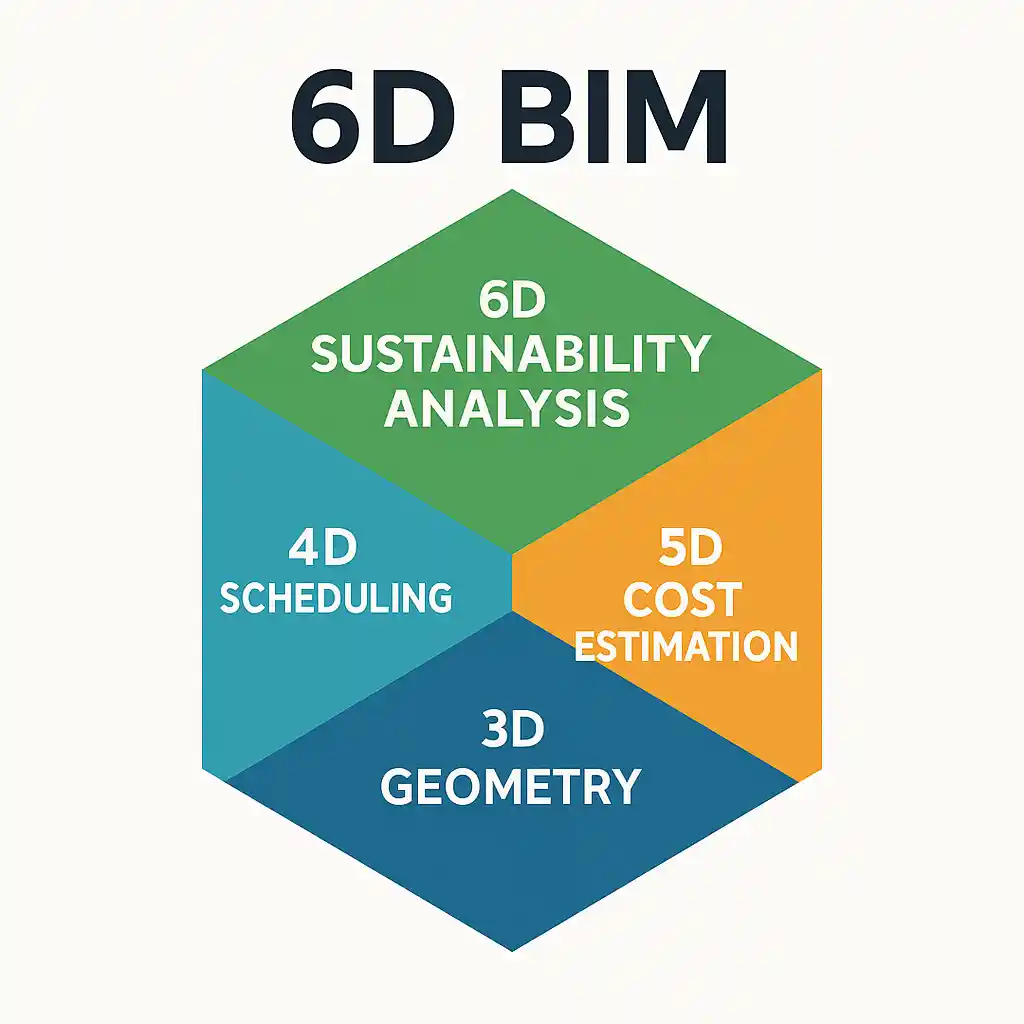
Incorporating the environmental data into the model allows project teams to model energy loads, evaluate natural light exposure, and investigate renewable energy possibilities all during the design phase. This results in more knowledgeable decisions that promote occupant comfort at the lowest operational cost. 6D BIM also aids in meeting green certification programmes.
What it does:
- Analyzes energy consumption, lighting, and HVAC efficiency
- Assists in selecting environmentally friendly materials
- Helps comply with green building standards (LEED, BREEAM)
Key Tools: IES VE, Green Building Studio, Sefaira
7D BIM – Facility Management and Asset Lifecycle
7D BIM extends BIM to support operation and maintenance throughout the building’s lifecycle. It serves facility managers and owners post-construction. Every asset—whether it’s a fire alarm, elevator, or HVAC unit—is embedded with relevant information such as manufacturer details, installation date, warranty, and service history. This comprehensive data repository makes it easy to plan preventive maintenance, order replacement parts, and respond to emergencies with minimal downtime.
For large facilities such as hospitals, universities, and airports, 7D BIM is a game-changer. It ensures that building systems continue to perform optimally, reduces lifecycle costs, and extends asset longevity. It also supports future renovations or retrofits by giving architects and engineers a detailed understanding of existing conditions. Integrating BIM with Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS) enables automation in maintenance scheduling and alerts.
What it does:
- Stores as-built data, specifications, warranties, and maintenance schedules
- Supports preventive maintenance and asset tracking
- Enhances long-term performance management of the facility
Key Tools: FM:Systems, Planon, Archibus, IBM Maximo
Summary Table of BIM Dimensions
| BIM Dimension | Key Focus | Value Addition |
| 3D | Geometry & Design | Visualization, Coordination, Clash Detection |
| 4D | Time | Construction Scheduling, Sequencing |
| 5D | Cost | Budget Control, Estimations |
| 6D | Sustainability | Energy Efficiency, Green Certifications |
| 7D | Facility Management | Lifecycle Management, Maintenance Planning |
Conclusion: Why Understanding BIM Dimensions Matters
In today’s data-driven construction landscape, mastering the various BIM dimensions—from 3D modeling to 7D lifecycle management—is no longer optional; it’s essential. Each dimension adds a new layer of insight, transforming the BIM model into a dynamic decision-making tool that spans every phase of a building’s life.
By integrating geometry, time, cost, sustainability, and facility management into a unified digital environment, stakeholders can work more collaboratively, minimize waste, reduce delays, and achieve better financial and environmental outcomes. These dimensions empower everyone, from architects and engineers to contractors and facility managers, to make smarter, faster, and more informed decisions. As projects become more complex and client expectations grow, understanding and leveraging BIM dimensions will be a key differentiator in delivering high-performance, future-ready buildings.